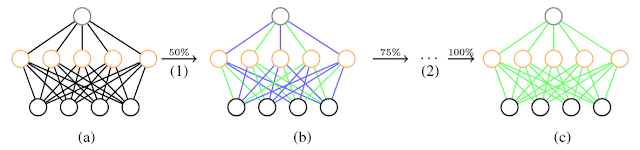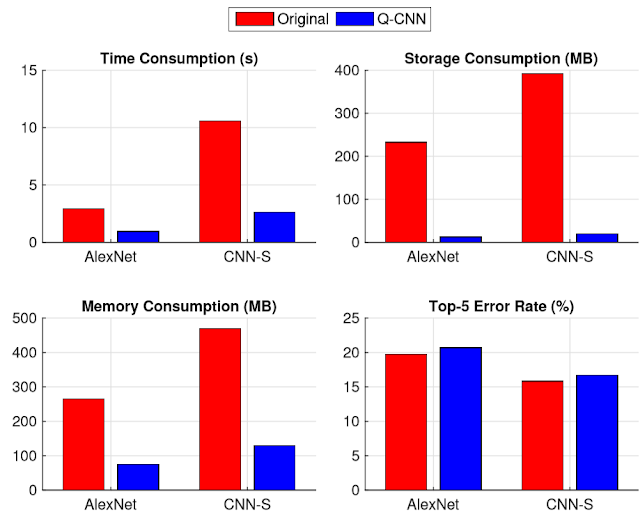
Quantized Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Devices cvpr 2016 1. Problem - CNN needs high performance hardware which prohibits their further extension (e.g. mobile service) 2. Solution - Simultaneously speed-up the computation and reduce the storage and memory overhead of CNN models > Quantized CNN 3. How - Quantized CNN + Both filter kernels in convolutional layers and weighting matrices in fully connected layers are quantized, aiming at minimizing the estimation error of each layer's response. 4. Performance - ILSVRC-12 + 4~6 X speed-up and 15 ~20 X compression with merely one percentage loss of classification accuracy - even mobile devices can accurately classify images within one second.